![]() customercare@normesdecodees.com
customercare@normesdecodees.com
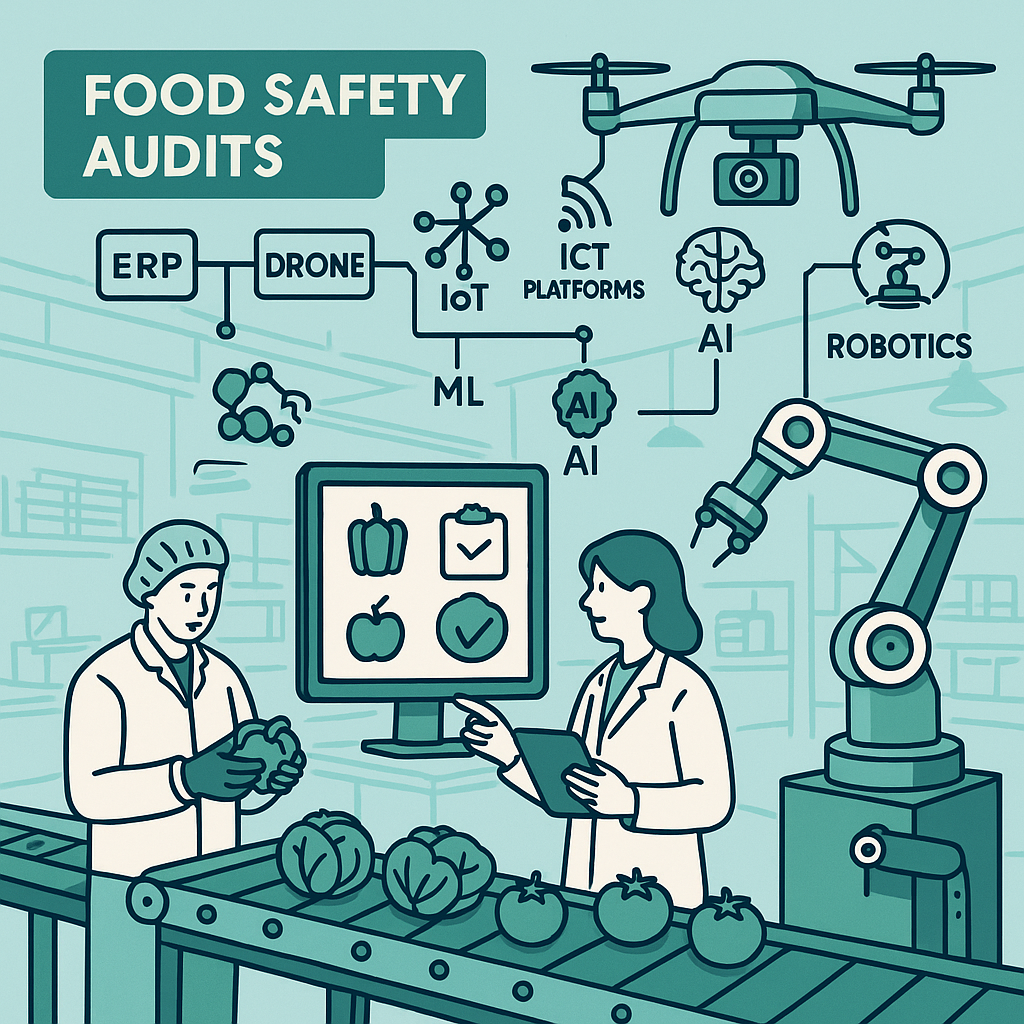
Food safety has always been built on prevention, verification, and trust. As global supply chains grow more complex and regulatory expectations become more stringent, traditional approaches alone are no longer sufficient. The future of food safety lies at the intersection of technology, data, and human expertise.
Emerging technologies such as ERP systems, drones, IoT, ICT platforms, machine learning (ML), artificial intelligence (AI), and robotics are redefining how food safety systems are designed, monitored, and audited. Rather than replacing professionals, these technologies will empower organizations to move from reactive compliance to predictive and proactive food safety management.
From Paper-Based Systems to Integrated ERP Platforms
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are becoming the backbone of modern food safety management. In the future, ERP platforms will not merely store documents but function as living food safety ecosystems.
- Real-time integration of HACCP plans, CCP monitoring, supplier approvals, and deviation management
- Automated alerts for non-conformances and overdue actions
- Seamless linkage between production, quality, maintenance, and procurement
For auditors and food safety teams, ERP-driven systems will provide instant traceability, enabling faster recalls, stronger root cause analysis, and data-backed decision-making.
Drones: The New Eyes in Food Safety Audits
Drones are set to revolutionize inspection and surveillance activities, especially in large facilities, warehouses, and logistics operations.
- Inspection of roofs, silos, pipelines, cold storage, and high-risk areas without human exposure
- Monitoring hygiene zones, pest-prone areas, drainage, and waste management
- Live visual evidence for internal audits and management reviews
- Monitoring of the cleaning and disinfection
- Monitoring of personal hygiene and personal habits
In the future, drone data may be directly linked with audit platforms, creating objective, time-stamped evidence that strengthens audit credibility.
Internet of Things (IoT): Real-Time Risk Monitoring
IoT devices will play a critical role in transforming food safety from periodic checks to continuous monitoring.
Examples include:
- Temperature, humidity, and pressure sensors in processing, storage, and transport
- Metal detector and X-ray performance monitoring
- Water quality and CIP system verification
- Microbiological and allergen monitoring
These smart sensors will feed data directly into ICT platforms, ensuring early detection of deviations and minimizing food safety incidents before they escalate.
ICT Platforms: Enabling Connected Audits and Collaboration
Information and Communication Technology (ICT) platforms will support remote audits, hybrid inspections, and global collaboration.
Key benefits include:
- Secure sharing of records, videos, and corrective actions
- Digital audit trails aligned with GFSI standards
- Faster communication between sites, auditors, certification bodies, and customers
ICT platforms will help organizations maintain compliance even during travel restrictions, emergencies, or multi-site operations.
Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence: Predicting the Next Risk
AI and ML will mark a shift from checklist-based compliance to risk intelligence.
Future applications include:
- Predicting food safety failures based on historical trends
- Identifying weak signals that humans may overlook
- Prioritizing audit focus areas based on risk ranking
Instead of asking “What went wrong?”, food safety teams will increasingly ask, “What is likely to go wrong next?”
Robotics: Precision, Consistency, and Hygiene
Robotics will enhance food safety by reducing human error and contamination risks.
- Automated cleaning and sanitation systems
- Robotic sampling for microbiological testing
- AI-assisted sorting and inspection
In high-risk environments, robotics will ensure consistent execution of critical food safety tasks, supporting both quality and worker safety.
The Human Element: Technology as an Enabler, Not a Replacement
While technology will transform food safety systems, people will remain at the centre. Leadership commitment, food safety culture, competence, and ethical behaviour cannot be automated.
The future belongs to professionals who:
- Understand both standards and digital tools
- Use data intelligently, not blindly
- Balance technological insights with practical judgement
Auditors, trainers, and food safety leaders will evolve into risk interpreters and system integrators, guiding organizations through digital transformation.
Conclusion: Building a Smarter, Safer Food System
The future of food safety is not just about compliance—it is about confidence, transparency, and resilience. Technology will enable faster decisions, stronger controls, and smarter audits, but success will depend on how well organizations integrate these tools into their food safety culture.Those who invest today in digital food safety systems, training, and leadership will be best positioned to meet tomorrow’s challenges—protecting consumers, brands, and businesses alike.
Author
Ashish Gaur contact: ashish.gaur@normesdecodees.com